- Maasai tribe live in enclosures called Enkang which contains ten to twenty small huts and is protected by fences or bushes
- Warrior-shaving ceremony is known as Eunoto in Masai language
- Traditionally Masai tribe do not bury their dead
- Maasai tribe live along the border of Kenya and Tanzania
- Massai people originated in the Nile valley reaching the Great Rift Valley in the 17th or 18th century
- Swahili is the official language of Kenya and Tanzania
- Traditionally, Masai people wore capes made from calf hides and sheepskin
- Maasai huts are very small
- Earlobe ceremony is known as Eudoto in Masai language
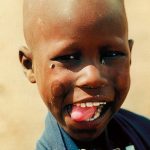
- The Masai tribe’s distinctive culture has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Swahili is the official language of Kenya
- The official language of Tanzania is Swahili
- Since 1960s, the Maasai tribe replaced animal-skin with cotton cloth
- Massai people originated in the Nile valley, leaving it in the 15th or 16th century and reaching the Great Rift Valley in the 17th or 18th century
- Masai language is called Maa
- Maasai live in huts that are very small with only one or two rooms not high enough for tall people to stand
- Warrior-shaving ceremony is called Eunoto in Masai language
- Oral law covers Maasai behavior
- The Maasai tribe has a long preserved culture
- The Maasai believe in a patriarchal society
- There are many ceremonies in Maasai tribe
- The Maasai tribe speaks Swahili, Man and English
- Maasai live in huts that are very small not high enough for tall people to stand
- Marriage is called Enkiama in Masai language
- The Masai God is called Enkai or Engai
- Maasai is a unique and popular tribe that has a long preserved culture
- Maasais live along the border of Kenya and Tanzania
- Maasai families live in enclosures called Enkang
- The Maasai people has a long preserved culture
- Massai tribe originated in the Nile valley, leaving it in the 15th or 16th century and reaching the Great Rift Valley in the 17th or 18th century
- The national language of Tanzania is Swahili
- Junior elder ceremony is called Olngesherr in Masai language
- Marriage is known as Enkiama in Masai language
- Although traditionally, Masai people wore capes made from calf hides and sheepskin, since 1960s they replaced animal-skin with cotton cloth
- Traditionally Masai tribe do not bury their dead because they believe that burials harm the soil
- Masai tribe’s distinctive culture has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Earlobe ceremony is called Enkigerunoto oo-inkiyiaa in Masai language
- Oral law dictates a large part of Maasai behavior
- Masai’s distinctiveness has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- The Maasai tribe reside in both Kenya and Tanzania
- The Maasai tribe are schooled in both English and Swahili
- Maasai families live in enclosures called Enkang which contains ten tow twenty small huts and are protected by fences or bushes with sharp thorns
- Some Maasai have become Muslim
- Traditionally Masai tribe do not bury their dead and are simply left outside for scavengers
- The Masai tribe’s distinctiveness has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Masai practice piercing and stretching of earlobes
- Masais believe that burials harm the soil and hence is reserved only for some chiefs
- There are many ceremonies among Maasai people including Eunoto, Eokoto e-kule, and Enkang oo-nkiri
- Circumcision is known as Emuratta in Masai language
- Two thirds of Maasai’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British
- Milk-drinking ceremony is called Eokoto e-kule in Masai language
- Masai are semi-nomadic people
- Maasai is a unique and popular tribe
- Massai tribe originated in Nile valley and left it in the 15th or 16th century
- Masais do not bury their dead
- Traditionally, Masai people wore capes made from calf hides and sheepskin decorated with glass beads
- Earlobe ceremony is called Eudoto in Masai language
- Masai tribe do not bury their dead
- The Masai’s distinctive culture and dress style has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Extensive oral law covers many aspects of Maasai behavior
- Maasai is a unique tribe that has a long preserved culture
- Traditionally Masais do not bury their dead
- Piercing and stretching of earlobes is the most common practice of the Maasai
- Masais’ Red God is called Engai Nanyokie
- Masai tribe’s strategic territory along the game parks has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Maasais live mainly in the game parks of East Africa
- Some Maasai have embraced Islam
- The Maasais reside in both Tanzania and Kenya
- Maasai territory reached its greatest size in the mid 1800’s
- Traditionally, Masai tribe wore capes made from calf hides and sheepskin
- Maasai clothing varies by place, age, and sex
- Swahili is the official language of Kenya and Tanzania
- Maasai tribe live in enclosures called Enkang that are protected by fences or bushes
- Maasais reside in both Tanzania and Kenya
- Earlobe ceremony is known as Enkigerunoto oo-inkiyiaa in Masai language
- Many Maasai have embraced Christianity
- Masai is a Kenyan tribal that belongs to the Nilotic ethnic group of nomadic people
- Maasai huts are very small with only one or two rooms not high enough for tall people to stand
- Masai’s distinctive dress style has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- The Maasai tribe are also schooled in English and Swahili
- Masais do not bury their dead and are simply left outside for scavengers
- Masai’s strategic territory along the game parks has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- The national language of Kenya and Tanzania is Swahili
- The Maasai tribe speaks Swahili, Maa and English
- Maasais reside in both Kenya and Tanzania
- Meat-eating ceremony is known as Enkang oo-nkiri in Masai language
- The Maasai reside in both Kenya and Tanzania
- A Masai’s wealth is measured in terms of children he has and cattle he owns
- There are many ceremonies in Maasai tribe including Olngesherr, Eudoto, and Enkigerunoto oo-inkiyiaa
- Massai people originated in Nile valley
- Masai tribe’s diet consists of raw meat, raw blood, and raw milk
- The Maasai reside in both Tanzania and Kenya
- Traditionally Masais do not bury their dead because they believe that burials harm the soil
- Maasai tribe is a unique tribe that has a long preserved culture
- Many Maasai have embraced Christianity as their religion
- There are about 900.000 Maasais in Kenya according to the 2009 census
- The Maasai believe in one god with a dual nature: a Black God called Engai Narok and a Red God called Engai Nanyokie
- Masai Mara, Kenya 1995 – large Herds of Wildebeest and Zebras. Scanned analogue Film Shot
- Maasai tribe live in enclosures called Enkang which contains ten to twenty small huts
- The Maasai believe in one god
- The semi-nomadic nature of Masai is due to their need to raise cattle and to find new grazing land
- Masai’s distinctive dress style and culture has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- The Maasai live along the border of Kenya and Tanzania
- Swahili is the national language of Tanzania
- The Masais believe that all the cattle in the world belongs to them
- Masais are warriors
- Oral law covers a large part of Maasai behavior
- The Masai tribe live along the border of Kenya and Tanzania
- Two thirds of the Maasai people’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British to create ranches for settlers
- Cattle is the primary source of food for the Masais
- Maasai huts are very small not high enough for tall people to stand
- The Maasai tribe are schooled in both Swahili and English
- Two thirds of Maasai people’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British
- Masai’s distinctive culture and dress style has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Extensive oral law covers Maasai behavior
- The Maasai language is called Maa
- Cattle is the primary source of food for the Masais and plays an important role in they lives
- There are many ceremonies in Maasai tribe including Ilkipirat, Eudoto, and Enkigerunoto oo-inkiyiaa
- The Maasai tribe speaks English, Maa and Swahili
- Masai is a Kenyan tribe
- Many Maasai have turned to Christianity
- Masais’ Black God is called Engai Narok and Red God is called Engai Nanyokie
- Maasai families live in enclosures which contains ten to twenty small huts and is protected by fences or bushes
- The Maasai believe in one god with a dual nature
- There are about 900.000 Maasais in Kenya
- Maasai territory covers all of the great rift valley
- Maasai tribe is a unique and popular tribe that has a long preserved culture
- There are many ceremonies among Maasai people including Eunoto, Eokoto e-kule, and Enkang oo-nkiri
- The Maasai is a popular tribe
- The Masais tribe live along the border of Kenya and Tanzania
- The Maasai tribe are also schooled in Swahili and English
- Masais tribe believe that burials harm the soil and hence is reserved only for some chiefs
- Massai tribe originated in Nile valley
- Massai tribe originated in the Nile valley reaching the Great Rift Valley in the 17th or 18th century
- According to the 2009 census there are about 900.000 Maasais living in Kenya
- Two thirds of Maasai tribe’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British
- The Maasai tribe reside in both Tanzania and Kenya
- Massai tribe left the Nile valley in the 15th or 16th century and reaching the Great Rift Valley in the 17th or 18th century
- Leg fire marks ceremony is called Ilkipirat in Masai language
- Two thirds of the Maasai tribe’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British
- The Masai’s distinctive dress style, culture and strategic territory along the game parks has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- According to the 2009 census there are about 900.000 Maasais in Kenya
- Maasai tribe live in enclosures which contains ten to twenty small huts and is protected by fences or bushes
- Traditionally, Masai tribe wore capes made from calf hides and sheepskin decorated with glass beads
- The Maasai believe in one god with a dual nature: a Black God called Engai Narok who is benevolent and and a Red God called Engai Nanyokie who is vengeful
- The Maasai tribe are schooled in Swahili and English
- Since 1960s, the Maasai people replaced animal-skin with cotton cloth
- There are many ceremonies in Maasai tribe including Enkipaata, Emuratta, and Enkiama
- Although traditionally, Masai tribe wore capes made from calf hides and sheepskin, since 1960s they replaced animal-skin with cotton cloth
- Despite civilization, western cultural influences, and education, the Maasai tribe have clung to their traditional ways
- Maasai tribe live in enclosures called Enkang
- Maasai tribe live in an enclosure
- Masai’s distinctive dress style, culture and strategic territory along the game parks has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- The Maasais live along the border of Kenya and Tanzania
- The Masai language Maa originates from the Nilo-Saharan language family
- Masai tribe’s distinctive dress style and culture has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- The Maasai tribe speaks Maa
- The Masai’s distinctive dress style and culture has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Although traditionally, Masai people wore capes made from calf hides and sheepskin decorated with glass beads, since 1960s they replaced animal-skin with cotton cloth
- Masai live mainly in Southern Kenya and Northern Tanzania
- The Masai tribe’s distinctive culture and dress style has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Two thirds of the Maasai’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British
- Maasai huts are very small with only one or two rooms
- The Masai tribe’s strategic territory along the game parks has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Maasai tribe live in enclosures called Enkang which contains ten tow twenty small huts and are protected by fences or bushes with sharp thorns
- There are many ceremonies in Maasai tribe including Eunoto, Eokoto e-kule, and Enkang oo-nkiri
- The Maasais reside in both Kenya and Tanzania
- The Maasai are semi-nomadic in nature
- The official language of Kenya is Swahili
- Maasai are pastoralists
- Oral law dictates Maasai behavior
- The Maasai tribe live along the border of Kenya and Tanzania
- The Maasai tribe speaks Maa, Swahili and English
- There are about 900.000 Maasais living in Kenya
- Extensive oral law dictates a large part of Maasai behavior
- Masai tribe do not bury their dead because they believe that burials harm the soil
- There are many ceremonies among Maasai people
- The national language of Tanzania and Kenya is Swahili
- Maasai tribe reside in both Tanzania and Kenya
- Masai tribe’s distinctiveness has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- The official language of Tanzania and Kenya is Swahili
- Despite western cultural influences, education, civilization, the Maasais have clung to their traditional ways
- Massai people left the Nile valley in the 15th or 16th century and reaching the Great Rift Valley in the 17th or 18th century
- Traditionally Masais do not bury their dead and are simply left outside for scavengers
- Masai tribe’s distinctive dress style has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Two thirds of Maasai people’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British to create ranches for settlers
- Piercing and stretching of earlobes is commonly practiced among the Maasai
- Single Acacia Tree in Masai Mara, Kenya. Film Shot made 1995, scanned.
- The Masais are constantly raising cattle and finding new grazing land
- The Maasai tribe is a popular tribe
- Masai are known for their distinctive customs and culture
- The Masai’s distinctiveness has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Extensive oral law dictates many aspects of Maasai behavior
- Maasai, Samburu and Kalenjin belong to the Nilotic group
- The Masai language Maa is closely related to Dinka and Nuer
- Maasai families live in an enclosure
- Maasai families live in enclosures called Enkang that are protected by fences or bushes with sharp thorns
- Massai people originated in Nile valley and left it in the 15th or 16th century
- Masai tribe do not bury their dead and are simply left outside for scavengers
- Oral law dictates many aspects of Maasai behavior
- Senior boy ceremony is known as Enkipaata in Masai language
- Single Acacia Tree in Masai Mara, Kenya. Film Shot made 1995, scanned
- Two thirds of the Maasai people’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British
- Maasai tribe is a popular tribe that has a long preserved culture
- Maasai is a unique tribe
- Masai tribe’s distinctive dress style, culture and strategic territory along the game parks has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Despite western cultural influences, civilization, and education, the Maasai tribe have clung to their traditional ways
- The Maasai are a Nilotic group
- The Maasai have a patriarchal society
- Two thirds of the Maasai tribe’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British to create ranches for settlers
- Swahili is the official language of Kenya
- The Maasai tribe are schooled in English and Swahili
- Despite western cultural influences, civilization, and education, the Maasais have clung to their traditional ways
- Masais do not bury their dead because they believe that burials harm the soil
- Milk-drinking ceremony is known as Eokoto e-kule in Masai language
- Some Maasai have embraced Islam as their religion
- Maasai tribe reside in both Kenya and Tanzania
- The Maasai is a unique tribe
- Meat-eating ceremony is called Enkang oo-nkiri in Masai language
- Swahili is the national language of Tanzania and Kenya
- Maasai, Samburu and Kalenjin are pastoralists
- The Maasai tribe speaks Maa, English and Swahili
- Senior boy ceremony is called Enkipaata in Masai language
- The Maasai believe in one god with a dual nature: Black God and Red God
- The Maasai is a unique and popular tribe
- Extensive oral law dictates Maasai behavior
- Masai Mara, Kenya 1995 – large Herds of Wildebeest and Zebras. Scanned analogue Film Shot.
- The Masai’s distinctive dress style has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- There are many ceremonies among Maasai people including Enkipaata, Emuratta, and Enkiama
- The Maasai tribe is a unique tribe
- Although traditionally, Masai tribe wore capes made from calf hides and sheepskin decorated with glass beads, since 1960s they replaced animal-skin with cotton cloth
- Leg fire marks ceremony is known as Ilkipirat in Masai language
- Two thirds of Maasai tribe’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British to create ranches for settlers
- Many Maasai have become Christian
- The Masai tribe’s distinctive dress style and culture has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Maasai families live in enclosures called Enkang which contains ten to twenty small huts and is protected by fences or bushes
- The Maasai tribe speaks English, Swahili and Maa
- Masai’s diet consists of raw meat, raw blood, and raw milk
- The official language of Kenya and Tanzania is Swahili
- The Masai’s strategic territory along the game parks has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- The important matters of Masais are decided by elder men
- Maasai is a popular tribe
- Two thirds of Maasai tribe’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British to create ranches for settlers and wildlife reserves and national parks
- Cattle is the primary source of food for the Masais tribe and plays an important role in they lives
- Masai tribe’s distinctive culture and dress style has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- There are many ceremonies among Maasai people including Ilkipirat, Eudoto, and Enkigerunoto oo-inkiyiaa
- Maasai families live in enclosures called Enkang that are protected by fences or bushes
- The Maasai are semi-nomadic
- Extensive oral law covers a large part of Maasai behavior
- Maasai is a popular tribe that has a long preserved culture
- Junior elder ceremony is known as Olngesherr in Masai language
- Maasai families live in enclosures called Enkang which contains ten to twenty small huts
- Circumcision is called Emuratta in Masai language
- Oral law covers many aspects of Maasai behavior
- Masais’ Black God is called Engai Narok
- The semi-nomadic nature of Masai tribe is due to their need to raise cattle and to find new grazing land
- Swahili is the national language of Kenya
- Maasai tribe live in enclosures called Enkang that are protected by fences or bushes with sharp thorns
- Maasai live in huts that are very small with only one or two rooms
- The Masai tribe’s distinctive dress style, culture and strategic territory along the game parks has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Swahili is the national language of Kenya and Tanzania
- Maasai s speak in a language called Maa
- Maasai, Kalanin and Samburu are pastoralists
- Masai’s distinctive culture has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- Massai tribe originated in Nile valley and left it in the 15th or 16th century
- Two thirds of the Maasai tribe’s land was taken away by the Kenyan government and the British to create ranches for settlers and wildlife reserves and national parks
- Masais practice cattle rustling because they believe that all the cattle in the world belongs to them
- The Masai tribe’s distinctive dress style has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
- The Masai’s distinctive culture has made them one of Kenya’s most internationally famous tourist attractions
5 facts about Maasai
- Maasais are warriors and cattle-rustlers
- Maasais practice circumcision
- Maasais use spears, shields and clubs for hunting
- Maasais live along the Great Rift Valley
- Many Maasais do not eat any vegetables or fruit at all
To receive a colourful digibook about Maasai with videos, images and text, please fill out the following form or simply email us on safaris@safari-center.com