Ear Barotrauma While Doing Balloon Safaris
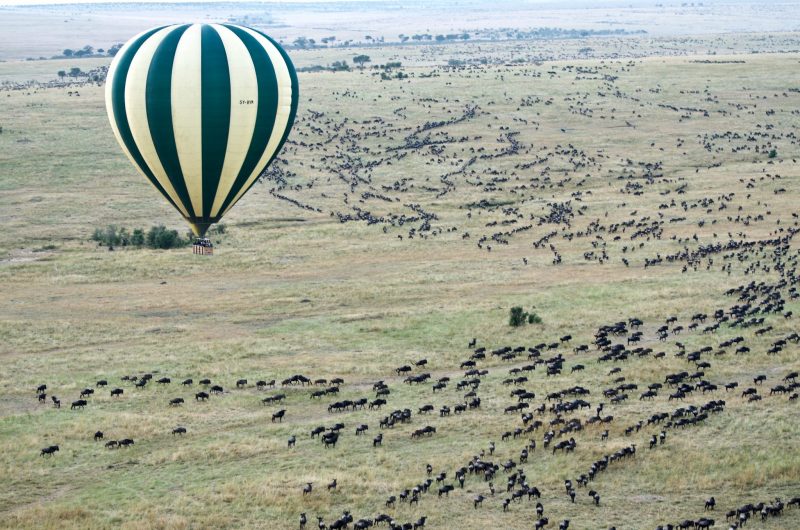
Enjoying Kenya safari in a hot air balloon is one of the most thrilling experiences. It gives a bird’s eye view of the wildlife and the vast savannah of the game parks in Kenya. After about an hour, just about the time of descent of the balloon, along with the exhilaration, some people feel a slight discomfort or stuffiness in the ear. But it almost always goes away on landing. This uneasiness is ear barotrauma. People who suffer from congested nose due to common cold are more likely than others to feel such awkwardness.
Ear barotrauma explained
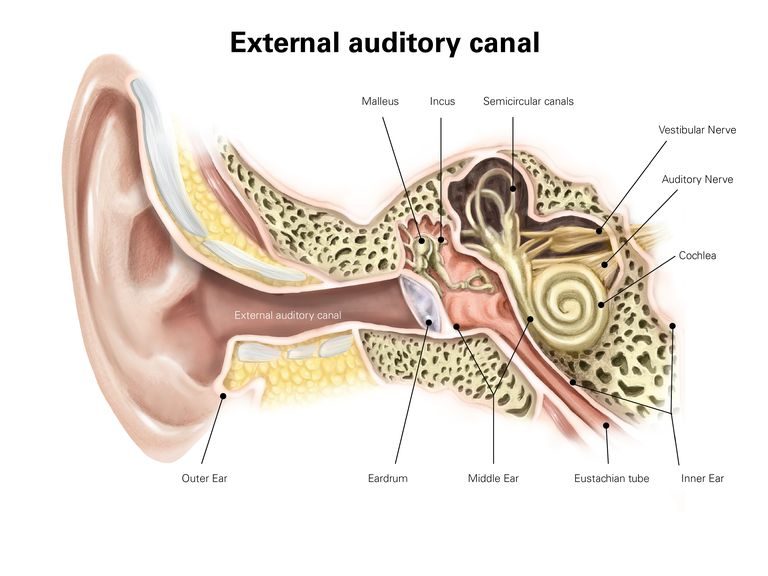
The eardrum separates the canal of the ear from the center ear. The small space behind the eardrum connects the back of the nose and throat through the Eustachian tube. Inside the ear, the air that fills the tympanic cavity is absorbed into the lining of the middle ear. Then it flows back up through the tube. This way the Eustachian tube connects the tympanic cavity with the throat and back of the nose. Ironically, this pipe also connects the middle ear to the outside world. So, the middle ear is separated from the external world by the eustachian tube anteromedially and the tympanic membrane laterally. Thus, this conduit facilitates air to enter when pressure equalization is needed. It also helps maintain and regulate air pressure by keeping the air on either side of the eardrum the same.
During balloon ride
Ear barotrauma while doing balloon safaris
The eardrum separates the canal of the ear from the center ear. The small space behind the eardrum connects the back of the nose and throat through the Eustachian tube. Inside the ear, the air that fills the tympanic cavity is absorbed into the lining of the middle ear. Then it flows back up through the tube. This way the Eustachian tube connects the tympanic cavity with the throat and back of the nose. Ironically, this pipe also connects the middle ear to the outside world. So, the middle ear is separated from the external world by the eustachian tube anteromedially and the tympanic membrane laterally. Thus, this conduit facilitates air to enter when pressure equalization is needed. It also helps maintain and regulate air pressure by keeping the air on either side of the eardrum the same.
Eustachian tube helps to restore equilibrium during pressure changes. It is the Eustachian tube that holds the ears in their normal state. Hence, equalization or normalization of pressure occurs through the soft tissue tube called the Eustachian tube. This extends from the middle ear space to the back of the nose.
Preventing ear barotrauma
If the Eustachian tube stays blocked, the middle ear can fill with clear fluid to try to equalize the pressure. This fluid called the serous otitis media that comes out of blood vessels lining the inner ear can only drain if the tube is open. In other words, prevention of ear barotrauma involves keeping the Eustachian tubes open. Otherwise, the pressure difference experienced during a balloon safari can create hearing difficulty and an uncomfortable feeling in the ear.
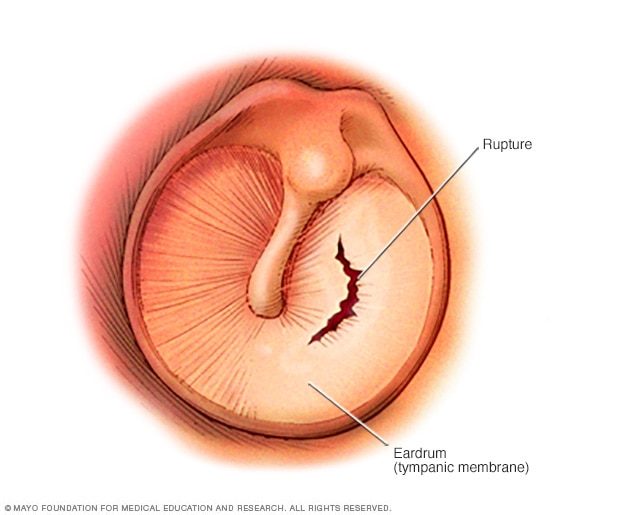
In some cases, it may bruise the eardrum or rupture the oval window Source: Mayo Clinic
Under normal circumstances, the air pressure outside the body is most often the same as that in the middle ear. When it matches with that of the middle ear, the tympanic membrane vibrates, and we hear a clear sound. But when a balloon lands, the pressure inside the cabin rises because the weight of the air is higher on the ground. To equalize, the pressure inside the middle ear also has to increase, which means air has to travel up the Eustachian tube into the middle ear.
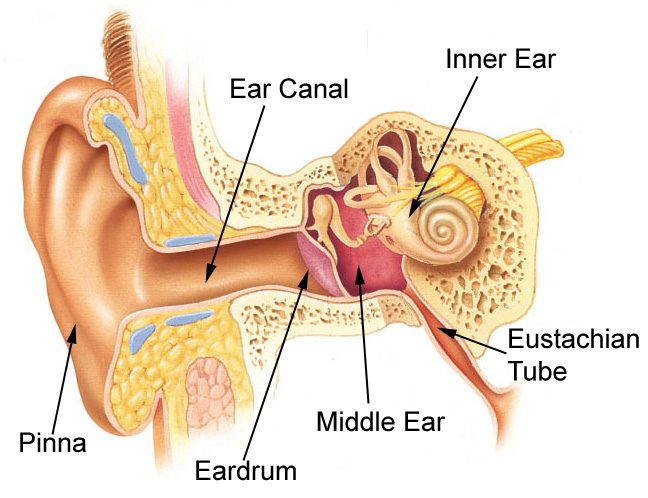
Eustachian tube Source: Hearing Health Associates
In case of a partial or complete blockage in the pipe due to a tumor, scarring, infection, allergy, or the common cold, air cannot pass through the middle ear. And the pressure on the outside remains different than the pressure in the middle ear. This obstruction in the tube leads to an inability to obtain equalization when the pressure changes fast during the balloon descent. In this case, the pressure differences create a vacuum, and the eardrum is stretched and sucked inward. And that is how variations in the air pressure between the outside world and the middle ear lead to discomfort, injury, and even hearing loss. In essence, ear barotrauma occurs when this tube does not function adequately.
Last resort measure
In extreme cases of ear barotrauma and if everything fails, surgery may be required and could be the best option for treatment to prevent permanent damage. This process stimulates airflow into the middle ear. People who frequently change altitudes or often fly for a living use it. The ear tube will remain in place for up to twelve months. Another option involves a tiny surgical slit cut into the eardrum that allows the pressure to equalize by removing any fluid. But this may not be a permanent solution as the slit will heal quickly.
Ear ache during balloon safari
To book a balloon safari, please fill out the following form or simply email us on safaris@safari-center.com





